Jupyter Notebook
Accessing Jupyter on compute nodes
Step 1 — Request an interactive reservation (e.g., GPU node)
salloc -A $SLURM_ACCOUNT -N1 -p gpu -t 1:00:00 srun --pty bash \
-c 'module purge; module load miniforge3/25.3.1; \
source $HOME_MINIFORGE/miniforge.rc; \
eval "$(mamba shell hook --shell bash)"; \
mamba activate dl_test; \
jupyter lab --no-browser --port=8888 --ip=0.0.0.0'
The environment above is provided as an example. Adapt the commands and the environment name (dl_test) to your setup.
Example output — note the token and the node name:
[I 2024-11-22 18:50:20.263 ServerApp] Jupyter Server 2.14.1 is running at:
[I 2024-11-22 18:50:20.263 ServerApp] http://node:8888/lab?token=0cd965...
Step 2 — Open the SSH tunnel from your local machine
ssh -fNL 8888:node:8888 -p <port> login@193.54.9.82
# enter the password if needed
- First port (local): 8888 (changeable if already in use).
node:8888: corresponds to the compute node and the Jupyter port.
Troubleshooting — occupied ports:
- Windows (cmd):
netstat -ano | findstr :<port>
taskkill /PID <pid> /F
- Linux:
ss -ltnp
kill -9 <pid>
Step 3 — Open the browser
Replace the node name in the URL provided by Jupyter with localhost. Example:
- Replace:
http://node:8888/lab?token=xxxx...
- With:
http://localhost:8888/lab?token=xxxx...
or, if you only forwarded the port without the token, open:
http://localhost:8888/lab?
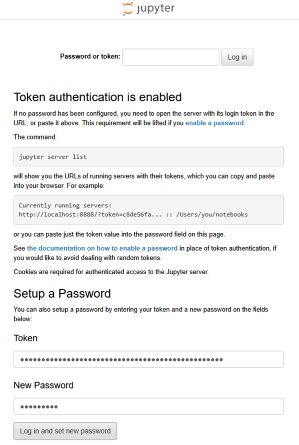
Keep the token displayed by Jupyter or copy the full URL to a secure file for reuse without restarting Jupyter.
On the node, run:
jupyter server password
then follow the prompts to set a password and avoid using the token at each startup.
In the browser, after a first login via http://localhost:8888, paste the token into the "Token" field then set a password in "New password" for future access.
If local port 8888 is already in use, pick a free port (e.g., 8889) and adjust the SSH command:
ssh -fNL 8889:node:8888 -p <port> login@193.54.9.82
then open http://localhost:8889.
Make sure your Python environment contains jupyter/jupyterlab installed:
mamba list | grep jupyter
(or conda list | grep jupyter depending on your manager)
Jupyter Lab provides a richer interface (files, terminals, visualizations) — use:
jupyter lab --no-browser --port=8888 --ip=0.0.0.0
- Adjust ports (
-pand--port) and the node name according to your configuration. - Never share the token or the public URL.